A novel approach to investigate how oxygen microenvironment changes during rice colonization by Magnaporthe oryzae
페이지 정보

조회 109회 작성일 25-05-08 15:45
본문
| Journal | Environmental Microbiology |
|---|---|
| Name | Hyunjung Chung, Seongbeom Kim, Ki-Tae Kim, Bae-Geun Hwang, Hyejeong Kim, Sang-Joon Lee and Yong-Hwan Lee |
| Year | 2019 |
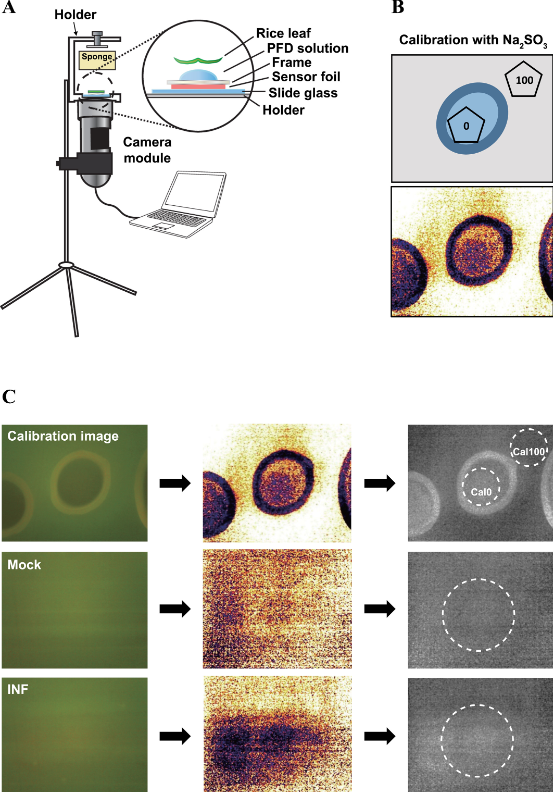
Because molecular oxygen functions as the final acceptor of electrons during aerobic respiration and a substrate for diverse enzymatic reactions, eukaryotes employ various mechanisms to maintain cellular homeostasis under varying oxygen concentration. Human fungal pathogens change the expression of genes involved in virulence and oxygen-required metabolisms such as ergosterol (ERG) synthesis when they encounter oxygen limitation (hypoxia) during infection. The oxygen level in plant tissues also fluctuates, potentially creating hypoxic stress to pathogens during infection. However, little is known about how in planta oxygen dynamics impact pathogenesis. In this study, we investigated oxygen dynamics in rice during infection by Magnaporthe oryzae via two approaches. First, rice leaves infected by M. oryzae were noninvasively probed using a microscopic oxygen sensor. Second, an immunofluorescence assay based on a chemical probe, pimonidazole, was used. Both methods showed that oxygen concentration in rice decreased after fungal penetration. We also functionally characterized five hypoxia-responsive genes participating in ERG biosynthesis for their role in pathogenesis. Resulting insights and tools will help study the nature of in planta oxygen dynamics in other pathosystems.